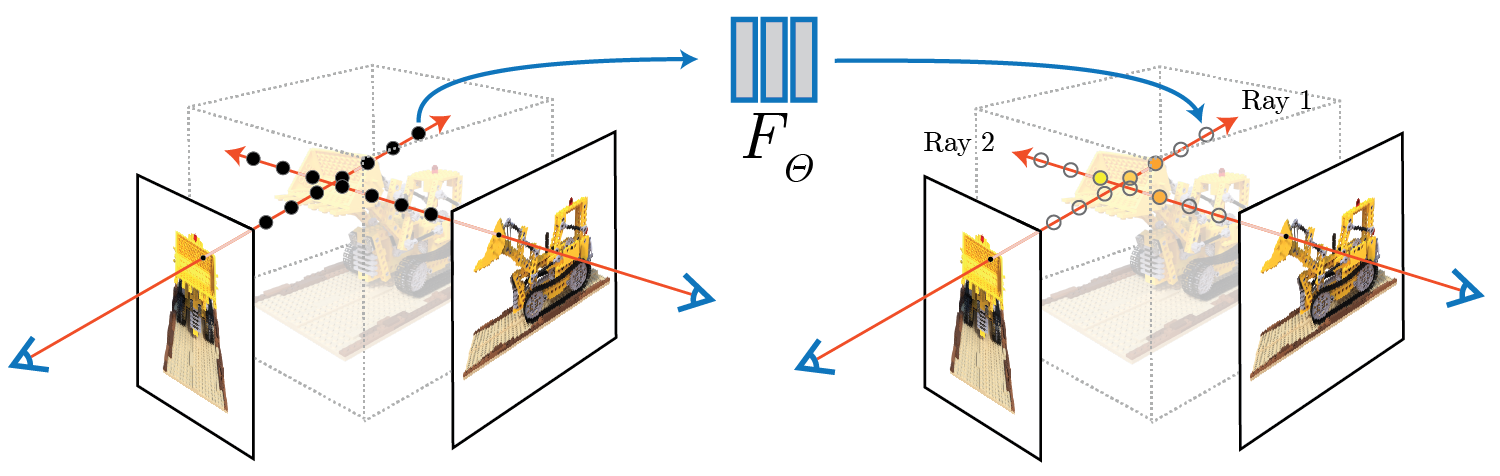
We’ve been exploring the dynamic world of 3D scanning and modeling and wanted to share some insights on two prominent technologies: NeRF (Neural Radiance Fields) and Photogrammetry.
NeRF represents a revolutionary approach in 3D technology. It utilizes deep learning to transform 2D images into highly realistic 3D models. This method is a significant departure from traditional 3D modeling, as it relies on sophisticated algorithms instead of physical scanners, offering an unprecedented level of detail and realism.
On the other hand, Photogrammetry, a more traditional technique, creates 3D models by stitching together multiple photographs taken from various angles. This method is renowned for its straightforwardness and effectiveness, making it a popular choice in fields like archaeology, architecture, and film.
The fundamental difference between NeRF and Photogrammetry is their modeling approach. Photogrammetry builds 3D models directly from photographs, while NeRF uses a neural network to interpret and reconstruct the 3D space from images, resulting in more intricate and life-like models.
Both technologies have unique strengths and are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in 3D scanning and modeling. It’s exciting to witness these advancements and consider their potential impact on various industries.
Read related articles: